Viindoo Accounting - Automate your accounting operations
Cash flow prediction, effective business financial planning. Closely integrate and real-time keep track of data.
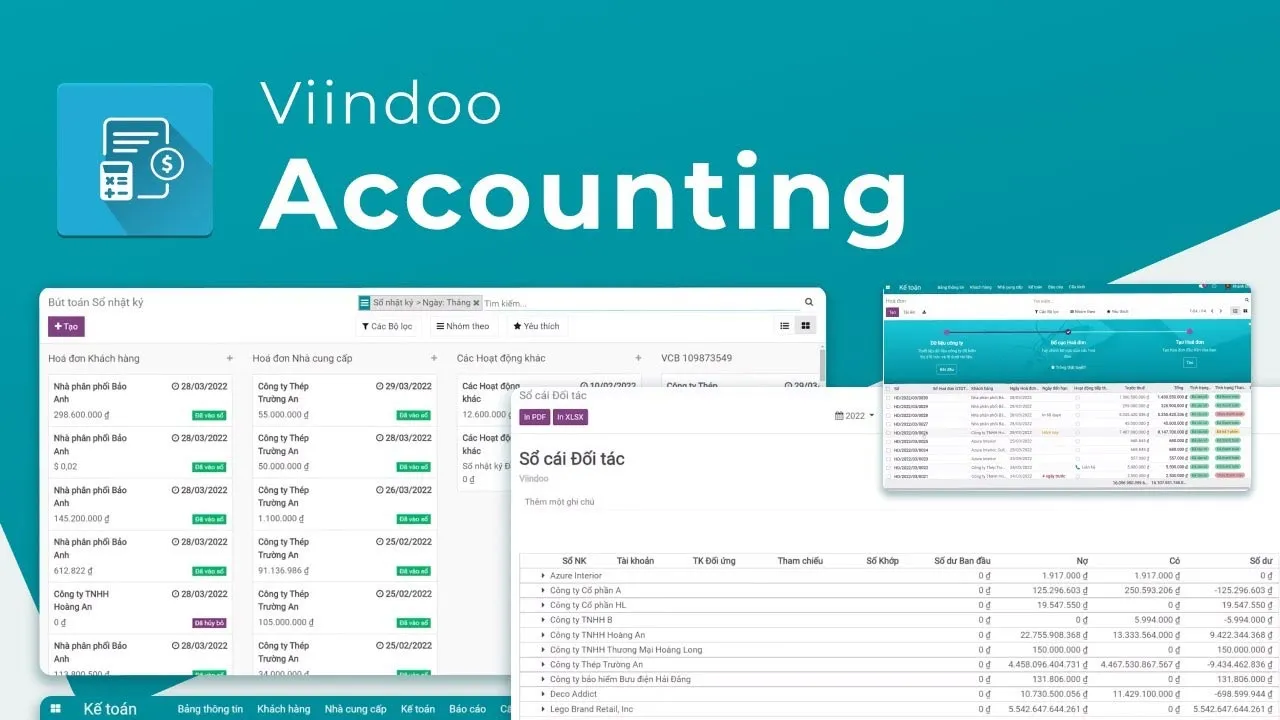
Automate all business accounting tasks.
Closely integrate and real-time keep track of data.
Comply with global accounting standards.
Cash flow prediction, effective business financial planning.
Automate business accounting task
Set up automatic transaction recording rules for each process, reduce mistakes of manual data entry at different stages, and speed up the data processing accurately, all achieved through the use of online accounting software.
Data is created only once from the beginning and used throughout the accounting process, which ensures accuracy and data-tracking ability at any time.
Automatically recommend reconciliation of matching amounts.
Smart filter, search tools help quickly find accounting information by multi-criteria.
Instantly automatic reporting systems help Managers capture accurate data by themselves.
Handle accounting tasks following Vietnamese accounting standards
Comply with Vietnamese Accounting Standards, Circular No. 200/2014/TT-BTC and Circular No. 133/2016/TT-BTC.
Manage, reconcile, and track changes in cash and bank integrated with payment activities.
Gather manufacturing cost based on data of Manufacturing application (BoM, manufacturing activities and process, etc.). Accounting entry incurred at the time of raw materials export, consumption record, and product import.
Record the payslip and payroll contribution in Payroll Application; make accurate, timely, and periodic salary data according to actual payment.
Integrated accounting management system: Tools to build and apply both accounting and financial management systems with different purposes:
Sum up revenue and expenses by project.
Gather and allocate costs by the purpose of payment, by department, by performed tasks, etc.
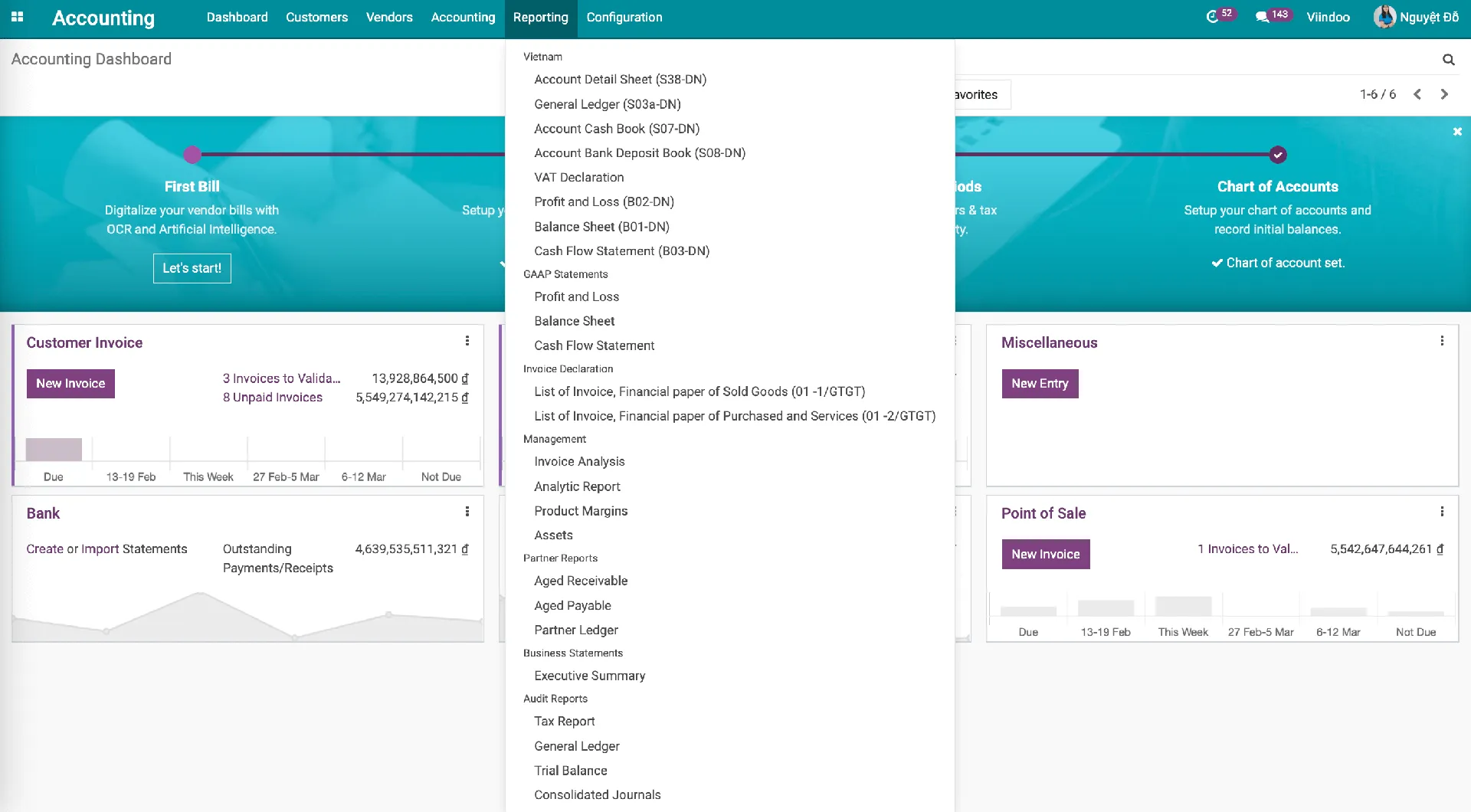
Inventory Accounting
Manage asset depreciation.
Track account payable, account receivable via invoices, payments, etc.
Spend less time on reconciliation and data audit.
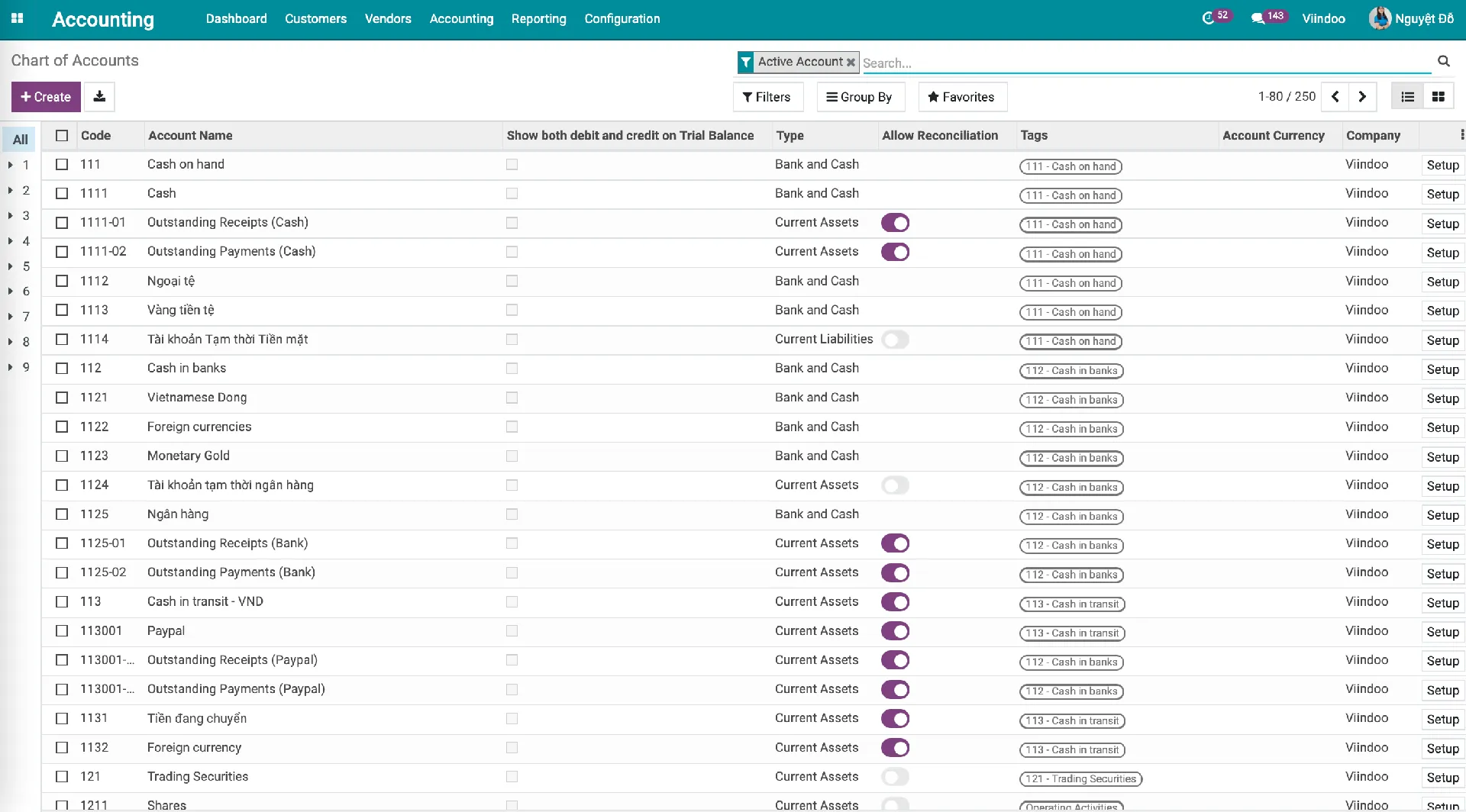
Country-specific accounting system
Viindoo Accounting brings various localized accounting systems adhering to country-specific accounting standards.
Multidimensional report, instant update
Instant, multi-dimensional data reporting by user levels.
Enable data comparison by the financial cycle, visualization of the financial trend over the months, periods, years, etc.
Enable data comparison by the financial cycle, visualization of the financial trend over the months, periods, years, etc.
Fully integrated with other applications

Sales
Manage quotations, orders, invoices, stock and customer payments.

Point of Sales
Create bills at Point of Sales and add them to Viindoo Accounting.

Inventory
Control inventory activities, automatically trigger replenishment in time.

Expense
Control employee expense, shorten the validating time & the management process.
Viindoo Accounting User Documentation
Accounting built for Growing Enterprises
Full control over finance, operations, and compliance in one unified system
